Study of the influence of tack resins on elastomeric formulations and applied evaluation methodologies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18226/23185279.e241303Keywords:
Elastomeric formulations, adhesion, tack, resinsAbstract
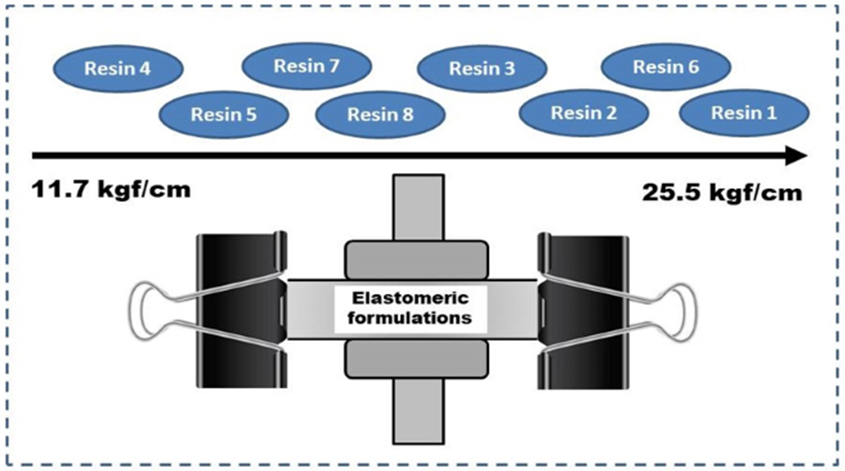
In this study, we examined the impact of eight distinct types of tack resins sourced from diverse origins (phenol-formaldehyde: SP – 1068, CRJ – 418, Koresin and SRF – 1501; hydrocarbons: Unilene A – 90 and Plastack RB 809; coumarone and breu) in several elastomeric formulations. For this purpose, it was developed a simple, robust and easily reproducible tack test employing synthetic rubber to assess these formulations. The elastomeric compounds were characterized by attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, rheometry, Mooney viscosity, crosslinking density by swelling in solvent, hardness, abrasion wear, tensile and tear strength, followed by tack tests. Overall, the formulations exhibited similar physical-mechanical properties. Regarding the tack test results, SP-1068 (phenol-formaldehyde) and Plastack RB 809 (hydrocarbon) resins demonstrated higher values, whereas the resorcinol-type phenol-formaldehyde presented a reduction of 10.7 %. Furthermore, interference from the functional groups in the resin’s chemical structure, difficulty in interacting with the matrix, and lower crosslink density were observed. In conclusion, the developed methodology proved satisfactory in yielding reliable and reproducible tack values.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Amanda Moresco, Nayrim Brizuela Guerra, Marcelo Giovanela, Suélen Moresco, Janaina Crespo (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Declaração de originalidade e cessão de direitos autorais
Declaro que o presente artigo é original, não está sendo tendo sido submetido à publicação em qualquer outro periódico nacional ou internacional durante o processo de revisão. Através deste instrumento, em meu nome e em nome dos demais co-autores, porventura existentes, cedo os direitos autorais do referido artigo à revista SCIENTIA CUM INDUSTRIA. Contudo, a reprodução total ou parcial impressa ou eletrônica pode ser feita desde que o autor comunique oficialmente à revista. Declaro estar ciente de que a não observância deste compromisso submeterá o infrator a sanções e penas previstas na Lei de Proteção de Direitos Autorias. Declaro estar ciente de que a não observância deste compromisso submeterá o infrator a sanções e penas previstas na Lei de Proteção de Direitos Autorias (Nº9610, de 19/02/1998).




