Incorporation of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide on the performance of hybrid polysulfone membranes for gas permeation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18226/23185279.e231105Keywords:
Additives, gas permeation, hybrid membranes, membrane separation process, permeabilityAbstract
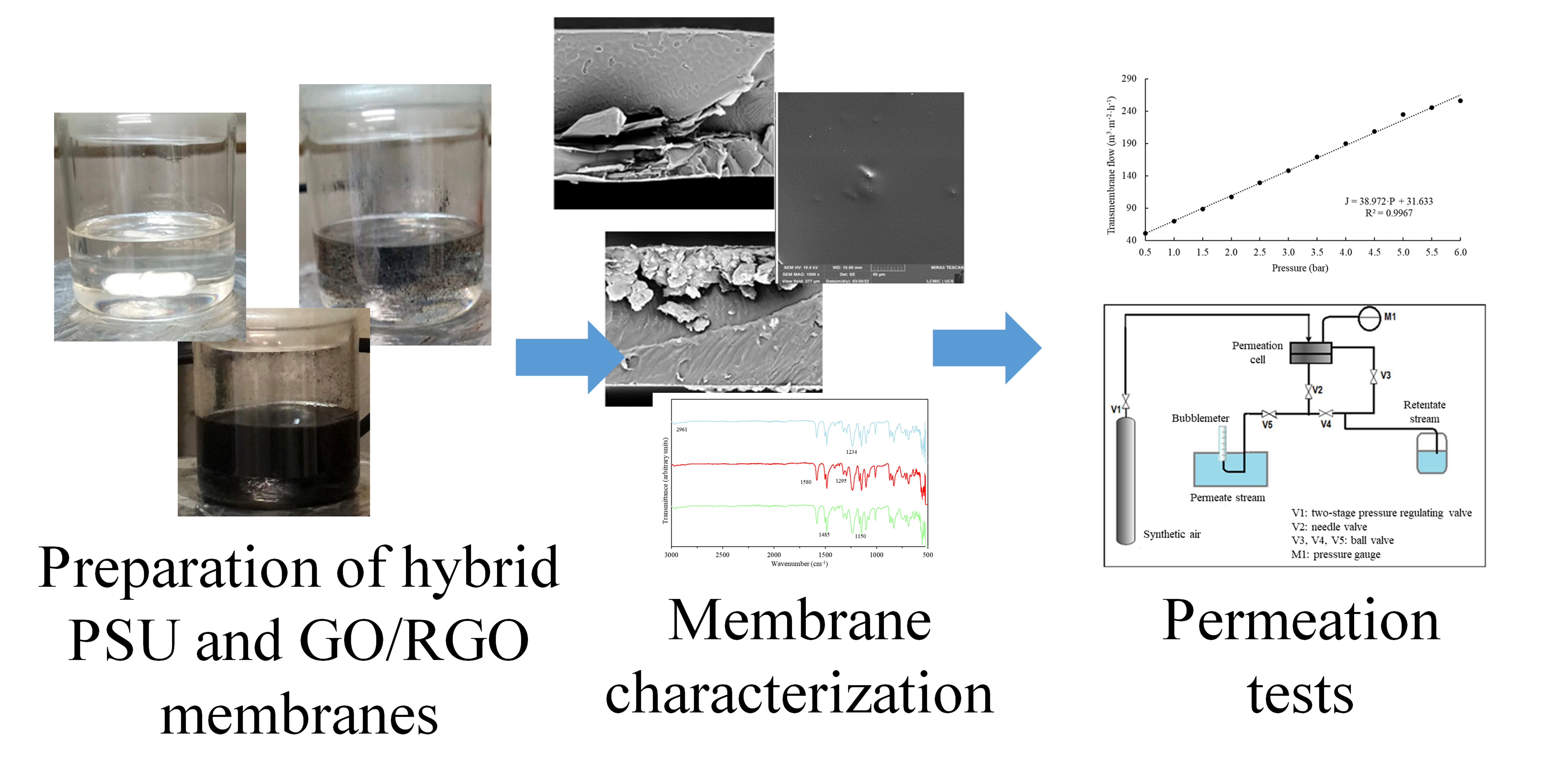
Polymeric membranes with the addition of graphene and derivatives are being studied due to the impacts on the physical-chemical and separation properties of these membranes. In this study, polysulfone (PSU) membranes containing graphene oxide (PSU/GO) and reduced graphene oxide (PSU/RGO) were developed at a concentration of 0.5 wt.%, to compare their characteristics and physical-chemical properties. Membrane morphology was evaluated by SEM, thermal stability by TGA/DTG, functional groups and material structure by FTIR, and mechanical properties by pressure test and gas permeation test using synthetic air. Agglomeration of GO and RGO was verified, a factor that may have interfered with the performance of the membranes. There was no change in thermal stability of the membranes with the presence of GO/RGO nor the occurrence of new bands observed in FTIR spectra, indicating that the interactions between PSU and GO/RGO were physical. All membranes resisted the maximum system pressure (6 bar), and it was not possible to identify whether the addition of graphene-derived materials had a positive effect on the mechanical strength. PSU/GO membranes had a better performance regarding synthetic air permeability during the gas permeation test than PSU and PSU/RGO membranes, possibly due to the functional groups present in GO.
Metrics
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Laís Gilioli Tosin, Wendel Paulo Silvestre, Camila Baldasso (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








