Biomonitoring the public supply reservoir in Camaquã ‒ RS using Tradescantia pallida var. purpurea and Escherichia coli
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18226/23185279.e251424Keywords:
Environmental monitoring, genotoxicity, water resources, environmental pollutionAbstract
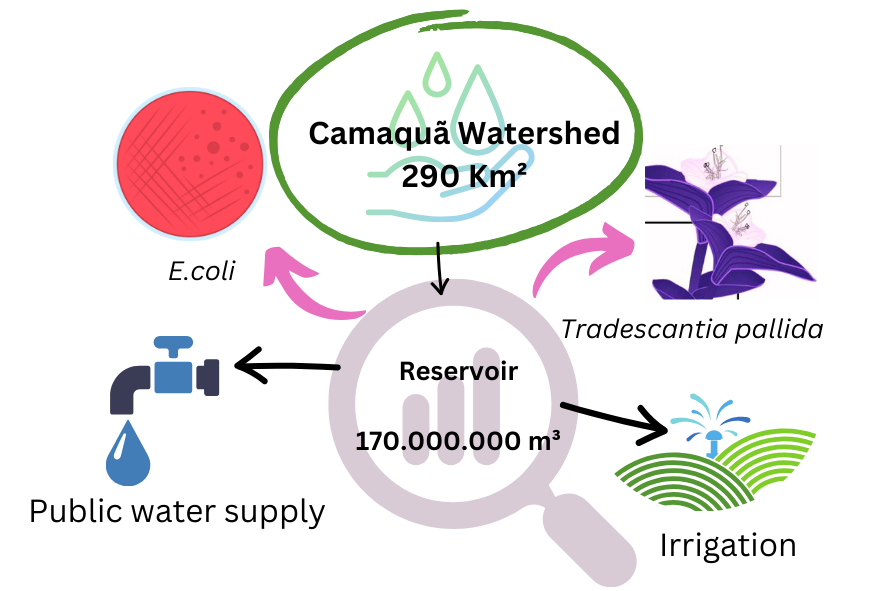
Water plays a central role in sustainable development, encompassing social, economic, and environmental dimensions: social, economic and environmental. The Arroio Duro Dam, located in the municipality of Camaquã - RS, is a reservoir that provides water for the public supply of approximately 60,000 inhabitants, in addition to enabling recreational activities and serving as a source of irrigation for agriculture. This work aims to evaluate the environmental quality of the Arroio Duro Dam using the determination of genotoxicity through pollen abortion in pollen grains of the bioindicator plant species Tradescantia pallida var. purpurea and the health quality bioindicator Escherichia coli. Preliminary results from two collections indicate high genotoxicity of the samples in relation to the negative control (p<0.05). Analyzes of the sanitary conditions of the Arroio Duro Dam indicated that the water is appropriate for the assigned uses, within the limits established by Brazilian legislation. This work highlights the importance of bioindicators in the integrated determination of environmental quality, generating results that assist in the integrated management of water resources in their multiple uses.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Daviline Caldasso da Silva, Giovanna Sampaio Laguna, Bárbara Nunes Flores Machado, Maria Eduarda Fortes Gonçalves , Carolina Dettmann Woloski, Caroline Neugebauer Wille, Luciana Rodrigues Nogueira

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Declaração de originalidade e cessão de direitos autorais
Declaro que o presente artigo é original, não está sendo tendo sido submetido à publicação em qualquer outro periódico nacional ou internacional durante o processo de revisão. Através deste instrumento, em meu nome e em nome dos demais co-autores, porventura existentes, cedo os direitos autorais do referido artigo à revista SCIENTIA CUM INDUSTRIA. Contudo, a reprodução total ou parcial impressa ou eletrônica pode ser feita desde que o autor comunique oficialmente à revista. Declaro estar ciente de que a não observância deste compromisso submeterá o infrator a sanções e penas previstas na Lei de Proteção de Direitos Autorias. Declaro estar ciente de que a não observância deste compromisso submeterá o infrator a sanções e penas previstas na Lei de Proteção de Direitos Autorias (Nº9610, de 19/02/1998).




